Installation Guide
Abstract
This document describes how to install AIMLFW, demo scenarios, it’s dependencies and required system resources.
Version history
Date |
Ver. |
Author |
Comment |
2022-11-30 |
0.1.0 |
First draft |
|
2023-06-06 |
1.0.0 |
Joseph Thaliath |
H Release |
2023-08-10 |
1.0.1 |
Joseph Thaliath |
H Maintenance release |
2023-12-14 |
1.1.0 |
Joseph Thaliath |
I release |
2023-12-14 |
2.0.0 |
Rajdeep Singh |
K release |
Introduction
This document describes the supported software and hardware configurations for the reference component as well as providing guidelines on how to install and configure such reference system.
The audience of this document is assumed to have good knowledge in AI/ML tools, Kubernetes and Linux system.
Hardware Requirements
Below are the minimum requirements for installing the AIMLFW
OS: Ubuntu 22.04 server
16 cpu cores
32 GB RAM
60 GB harddisk
Software Installation and Deployment
git clone [-b <branch-name>] "https://gerrit.o-ran-sc.org/r/aiml-fw/aimlfw-dep" # latest release branch is k-release
cd aimlfw-dep
Update recipe file RECIPE_EXAMPLE/example_recipe_latest_stable.yaml which includes update of VM IP and datalake details.
Ensure image version is correct.
Note: In case the Influx DB datalake is not available, this can be skipped at this stage and can be updated after installing datalake.
bin/install_traininghost.sh
Check running state of all pods and services using below command :
~$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
kubeflow cache-deployer-deployment-cf9646b9c-jxlqc 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow cache-server-56d4959c9-sz948 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow leofs-bfc4794f5-7xfdn 1/1 Running 0 56m
kubeflow metadata-envoy-deployment-9c7db86d8-7rlkf 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow metadata-grpc-deployment-d94cc8676-mhw4l 1/1 Running 5 (47m ago) 53m
kubeflow metadata-writer-cd5dd8f7-6qsx6 1/1 Running 1 (46m ago) 53m
kubeflow minio-5dc6ff5b96-4f9xd 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow ml-pipeline-85b6bf5f67-5x9lq 1/1 Running 2 53m
kubeflow ml-pipeline-persistenceagent-fc7c944d4-bjz5n 1/1 Running 1 (46m ago) 53m
kubeflow ml-pipeline-scheduledworkflow-676478b778-h42kx 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow ml-pipeline-ui-76bc4d6c99-8rw9x 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow ml-pipeline-viewer-crd-8574556b89-g5xw7 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow ml-pipeline-visualizationserver-5d7c54f495-mhdtj 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow mysql-5b446b5744-mcqlw 1/1 Running 0 53m
kubeflow workflow-controller-679dcfdd4f-c64bj 1/1 Running 0 53m
traininghost aiml-dashboard-667c546669-rslbz 1/1 Running 0 38m
traininghost aiml-notebook-5689459959-hd8r4 1/1 Running 0 38m
traininghost cassandra-0 1/1 Running 0 41m
traininghost data-extraction-bd7dc6747-98ddq 1/1 Running 0 39m
traininghost kfadapter-75c88574d5-ww7qb 1/1 Running 0 38m
traininghost modelmgmtservice-56874bfc67-ct6lk 1/1 Running 0 38m
traininghost tm-757bf57cb-rlx7v 1/1 Running 0 39m
traininghost tm-db-postgresql-0 1/1 Running 0 53m
Note: In K Release, dashboard is not supported. We recomment to use cURL to interact with AIMLFW components. Details are provided in further section for each operation required for model training.
Software Uninstallation & Upgrade
Run the following script to uninstall the traininghost:
bin/uninstall_traininghost.sh
To update the AIMLFW component, you need to follow a series of steps to ensure that the new changes are properly installed and integrated.
# Step 1: Uninstall the existing AIMLFW component
bin/uninstall.sh
# Step 2: Update the RECIPE_EXAMPLE/example_recipe_latest_stable.yaml file
# Make necessary changes to the recipe file here
# Step 3: Reinstall the AIMLFW component with the updated recipe
bin/install.sh -f RECIPE_EXAMPLE/example_recipe_latest_stable.yaml
DataLake Installation
In the context of AIMLFW, a datalake can be used to store and manage large amounts of data generated by various sources.
This section provides a detailed guide on how to install and configure a datalake for AIMLFW. Currently we support following methods to injest data for model-training: Standalone InfluxDB Installation and Prepare Non-RT RIC DME as a Data Source for AIMLFW.
1. Install Influx DB as datalake (Optional)
Standalone Influx DB can be installed using the following commands:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm install my-release bitnami/influxdb --version 5.13.5
~$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
my-release-influxdb-85888dfd97-77dwg 1/1 Running 0 15m
Use the following command to get INFLUX_DB_TOKEN which is required while creating feature-group.
kubectl get secret my-release-influxdb -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-user-token}" | base64 --decode
This section provides a detailed guide to onboard test-data to execute model-training.
Execute below from inside Influx DB container to create a bucket:
# INFLUX_DB_TOKEN is referred to the influxDb-token collected in previous step:
kubectl exec -it <influxdb-pod-name> -- influx bucket create -n UEData -o primary -t <INFLUX_DB_TOKEN>
Note: This Bucket name UEData will be reffered while creating featureGroup in further-steps.
Install the following dependencies which is required for parsing and onboarding data from .csv file:
sudo pip3 install pandas
sudo pip3 install influxdb_client
Use the insert.py in ric-app/qp repository to upload the qoe data in Influx DB
git clone -b f-release https://gerrit.o-ran-sc.org/r/ric-app/qp
cd qp/qp
Overwrite insert.py file with the following content:
import pandas as pd
from influxdb_client import InfluxDBClient
from influxdb_client.client.write_api import SYNCHRONOUS
import datetime
class INSERTDATA:
def __init__(self):
self.client = InfluxDBClient(url = "http://localhost:8086", token="<INFLUX_DB_TOKEN>")
def explode(df):
for col in df.columns:
if isinstance(df.iloc[0][col], list):
df = df.explode(col)
d = df[col].apply(pd.Series)
df[d.columns] = d
df = df.drop(col, axis=1)
return df
def jsonToTable(df):
df.index = range(len(df))
cols = [col for col in df.columns if isinstance(df.iloc[0][col], (dict, list))]
if len(cols) == 0:
return df
for col in cols:
d = explode(pd.DataFrame(df[col], columns=[col]))
d = d.dropna(axis=1, how='all')
df = pd.concat([df, d], axis=1)
df = df.drop(col, axis=1).dropna()
return jsonToTable(df)
def time(df):
df.index = pd.date_range(start=datetime.datetime.now(), freq='10ms', periods=len(df))
df['measTimeStampRf'] = df['measTimeStampRf'].astype(str)
return df
def populatedb():
df = pd.read_json('cell.json.gz', lines=True)
df = df[['cellMeasReport']].dropna()
df = jsonToTable(df)
df = time(df)
db = INSERTDATA()
write_api = db.client.write_api(write_options=SYNCHRONOUS)
write_api.write(bucket="UEData",record=df, data_frame_measurement_name="liveCell",org="primary")
populatedb()
Update <INFLUX_DB_TOKEN> in insert.py with the influxDb-token collected in previous step.
Follow below command to port forward for the script to access Influx DB (as no NodePort is exposed for InfluxDb)
kubectl port-forward svc/my-release-influxdb 8086:8086
Execute the following script to onboard test-data to local influxDb:
python3 insert.py
To check inserted data in Influx DB , execute below command inside the Influx DB container:
# Token is referred to the acess-token collected in previous step:
kubectl exec -it <influxdb-pod-name> -- influx query 'from(bucket: "UEData") |> range(start: -1000d)' -o primary -t <INFLUX_DB_TOKEN>
Result: _result
Table: keys: [_start, _stop, _field, _measurement]
_start:time _stop:time _field:string _measurement:string _time:time _value:int
------------------------------ ------------------------------ ---------------------- ---------------------- ------------------------------ --------------------------
2022-05-18T12:52:18.008858111Z 2025-02-11T12:52:18.008858111Z availPrbDl liveCell 2025-01-23T17:01:22.563381000Z 45
2022-05-18T12:52:18.008858111Z 2025-02-11T12:52:18.008858111Z availPrbDl liveCell 2025-01-23T17:01:22.573381000Z 91
2022-05-18T12:52:18.008858111Z 2025-02-11T12:52:18.008858111Z availPrbDl liveCell 2025-01-23T17:01:22.583381000Z 273
2022-05-18T12:52:18.008858111Z 2025-02-11T12:52:18.008858111Z availPrbDl liveCell 2025-01-23T17:01:22.593381000Z 53
Prepare Non-RT RIC DME as data source for AIMLFW (optional)
Please refer to the RANPM Installation Guide to install NonRtRic’s RANPM and Prepare the DME as a data-soruce for AIMLFW.
Feature Group Creation
A Feature Group is a logical entity to represent structured dataset, often stored in a Feature Store, to ensure consistency and reusability across different ML models and pipelines.
Following is the cURL request to create a feature group.
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/featureGroup' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"featuregroup_name": "<Name of the feature group>",
"feature_list": "<Features in a comma separated format>",
"datalake_source": "<DATALAKE_SOURCE>",
"enable_dme": <True for DME use, False for Standalone Influx DB>,
"host": "<IP of VM where Influx DB is installed>",
"port": "<Port of Influx DB>",",
"dme_port": "<If DME is True, then it refers to the Nodeport of InformationService (in RANPM)>",
"bucket": "<Bucket Name>",
"token": "<INFLUX_DB_TOKEN>",
"source_name": "<If DME is True, any source name. but same needs to be given when running push_qoe_data.sh>",
"measured_obj_class": "<Applicable in case of DME>",
"measurement": "<Measurement of the db that contains your features>",
"db_org": "<Org of the db>"
}'
Below are two examples covering supported scenarios for Data Injestion.
1. Non-RT RIC DME based feature group creation for Qoe Usecase
curl --location '<AIMLFW-Ip>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/featureGroup' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"featuregroup_name": "<FEATURE_GROUP_NAME>",
"feature_list": "x,y,pdcpBytesDl,pdcpBytesUl",
"datalake_source": "InfluxSource",
"enable_dme": true,
"host": "<RANPM-IP>",
"port": "8086",
"dme_port": "31823",
"bucket": "pm-logg-bucket",
"token": "<INFLUX_DB_TOKEN>",
"source_name": "",
"measured_obj_class": "NRCellDU",
"measurement": "test,ManagedElement=nodedntest,GNBDUFunction=1004,NRCellDU=c4_B13",
"db_org": "est"
} '
2. Standalone Influx DB based feature group creation for Qoe Usecase.
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/featureGroup' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"featuregroup_name": "<Feature Group name>",
"feature_list": "pdcpBytesDl,pdcpBytesUl",
"datalake_source": "InfluxSource",
"enable_dme": false,
"host": "my-release-influxdb.default",
"port": "8086",
"dme_port": "",
"bucket": "UEData",
"token": "<INFLUX_DB_TOKEN>",
"source_name": "",
"measured_obj_class": "",
"measurement": "liveCell",
"db_org": "primary"
}'
Register Model
A model MUST be registered to the Model-Management-Service (MME) before submitting any training request. A model is uniquely identified by modelName and modelVersion. Following is the sample cURL request to be used for registering the model.
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32006/ai-ml-model-registration/v1/model-registrations' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"modelId": {
"modelName": "modeltest1",
"modelVersion": "1"
},
"description": "This is a test model.",
"modelInformation": {
"metadata": {
"author": "John Doe"
},
"inputDataType": "pdcpBytesDl,pdcpBytesUl",
"outputDataType": "pdcpBytesDl,pdcpBytesUl"
}
}'
# inputDataType & outputDataType represents the input(features) & output for trainedModels.
# Note: Currently, outputDataType is not fucntionality used in implementation.
Model Discovery
This section describes model-discovery and its various options.
To fetch all registered models, use the following API endpoint:
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32006/ai-ml-model-discovery/v1/models'
To fetch models with modelName, use the following API endpoint:
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32006/ai-ml-model-discovery/v1/models?model-name=<model_name>'
To fetch specific model, use the following API endpoint:
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32006/ai-ml-model-discovery/v1/models?model-name=<model_name>&&model-version=<model_version>'
Onboarding Training/Re-Training Pipelines
Training and retraining pipelines in AIMLFW (AI/ML Framework for O-RAN SC) are structured sequences of steps designed to train or retrain ML models. These pipelines automate the execution of data processing, model training, evaluation, and storage, ensuring a streamlined workflow.
1. Onboard Pre-Existing Pipeline
AIMLFW does not come preloaded with the qoe-pipeline (responsible for model training) and qoe-pipeline-retrain-2 (responsible for model retraining). These pipelines need to be manually onboarded before they can be used in AIMLFW workflows.
Steps to Onboard Pre-existing Pipelines:
1. Access the Jupyter Dashboard Open a web browser and navigate to: http://<VM-Ip of AIMLFW>:32088/tree?
2. Load the Required Notebook Locate the notebook corresponding to each pipeline: qoe-pipeline for training qoe-pipeline-retrain-2 for retraining
3. Execute the Notebook Cells Open the respective notebook. Run all the cells in the notebook sequentially.
This process registers the pipeline in Kubeflow so it can be used by AIMLFW. Once these steps are completed, the pipelines will be available for use within AIMLFW training operations.
2. Onboard Custom Pipeline (Optional)
Following is a sample pseudo-code for a custom pipeline which user can implement and onboard.
from kfp import dsl
from kfp.compiler import Compiler
from kubernetes import client as k8s_client
@dsl.pipeline(
name="Model Training Pipeline",
description="A sample pipeline for training a machine learning model"
)
def training_pipeline():
# Implement the trainingPipeline Here
# Compile the pipeline to yaml-file
Compiler().compile(training_pipeline, "<OutputFile.yaml>")
# Upload Pipeline to AIMLFW
import requests
requests.post("http://<VM-Ip where AIMLFW is installed>:32002/pipelines/<Training_Pipeline_Name>/upload", files={'file':open("<OutputFile.yaml>",'rb')})
One can refer kubeflow documentation for implementing your pipeline.
Training job creation with DME or Standalone InfluxDB as data source
Creating a training job in AIMLFW involves defining the training pipeline, specifying the necessary configurations, and submitting the job for execution. The user needs to provide essential parameters. Once submitted, the pipeline runs within Kubeflow, leveraging AIMLFW’s orchestration capabilities to manage the training workflow. The status and progress of the training job can be monitored through logs.
You can create a TrainingJob using the following cURL command:
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/training-jobs' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"modelId":{
"modelname": "modeltest1",
"modelversion": "1"
},
"model_location": "",
"training_config": {
"description": "trainingjob for testing",
"dataPipeline": {
"feature_group_name": <Name of FeatureGroup created >,
"query_filter": "<This query-filter will be used to filter/transform your features>",
"arguments": {"epochs": 1}
},
"trainingPipeline": {
"training_pipeline_name": "qoe_Pipeline",
"training_pipeline_version": "qoe_Pipeline",
"retraining_pipeline_name":"qoe_Pipeline_retrain",
"retraining_pipeline_version":"qoe_Pipeline_retrain"
}
},
"training_dataset": "",
"validation_dataset": "",
"notification_url": "",
"consumer_rapp_id": "",
"producer_rapp_id": ""
}'
Following is the example used for Standalone-InfluxDb as a Data-Source:
curl --location 'http://<VM IP where AIMLFW is installed>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/training-jobs' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"modelId":{
"modelname": "modeltest1",
"modelversion": "1"
},
"model_location": "",
"training_config": {
"description": "trainingjob for testing",
"dataPipeline": {
"feature_group_name": <Name of FeatureGroup created >,
"query_filter": "",
"arguments": {"epochs": 1}
},
"trainingPipeline": {
"training_pipeline_name": "qoe_Pipeline",
"training_pipeline_version": "qoe_Pipeline",
"retraining_pipeline_name":"qoe_Pipeline_retrain",
"retraining_pipeline_version":"qoe_Pipeline_retrain"
}
},
"training_dataset": "",
"validation_dataset": "",
"notification_url": "",
"consumer_rapp_id": "",
"producer_rapp_id": ""
}'
Obtain the Status of Training Job
The Status of Trainingjob can be fetched using the following API endpoint. Replace <TrainingjobId> with the ID of the training job which is collected from response of the previous request.
curl --location http://<AIMLFW-Ip>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/training-jobs/<TrainingjobId>/status
Obtain Model URL for deploying trained models
You can curl the following API endpoint to obtain Trainingjob Info and fetch model_url for deployment after training is complete. Replace <TrainingjobId> with the ID of the training job.
curl --location 'http://<AIMLFW-Ip>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/training-jobs/<TrainingjobId>'
OR you can download the model using Model_name, Model_version, Model_artifact_version as follows:
wget http://<AIMLFW-Ip>:32002/model/<MODEL_NAME>/<MODEL_VERSION>/<MODEL_ARTIFACT_VERSION>/Model.zip
Model-Retraining
Retraining is the process of updating an existing model by incorporating new data or refining its parameters to improve performance. In AIMLFW, retraining jobs follow a structured pipeline similar to training but leverage previously trained models as a starting point. Users need to specify the retraining pipeline
A previously trained model can be retrained with different configurations/data as follows:
curl --location '<AIMLFW-Ip>:32002/ai-ml-model-training/v1/training-jobs' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"modelId": {
"modelname":"<MODEL_TO_RETRAIN>",
"modelversion":"<MODEL_VERSION_TO_RETRAIN>"
},
"training_config": {
"description": "Retraining-Example",
"dataPipeline": {
"feature_group_name": "<FEATUREGROUP_NAME>",
"query_filter": "",
"arguments": {"epochs": 20}
},
"trainingPipeline": {
"training_pipeline_name": "qoe_Pipeline",
"training_pipeline_version": "qoe_Pipeline",
"retraining_pipeline_name": "qoe_Pipeline_retrain",
"retraining_pipeline_version": "qoe_Pipeline_retrain"
}
},
"model_location": ""
}'
Verify Updated Artifact-Version after retraining from MME
curl --location '<AIMLFW-Ip>:32006/ai-ml-model-discovery/v1/models/?model-name=<MODEL_NAME>&model-version=<MODEL_VERSION>'
Below state diagram captures the flow for model state for training/training.
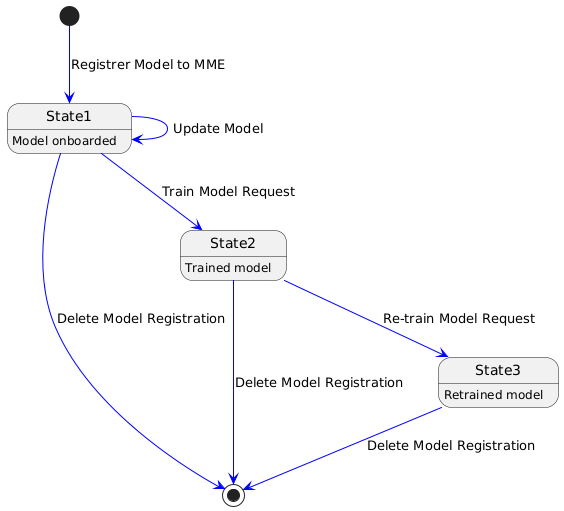
@startuml
[*] -[#blue]-> State1 : Registrer Model to MME
State1 -[#blue]-> State1 : Update Model
State1 -[#blue]-> [*] : Delete Model Registration
State1 : Model onboarded
State1 -[#blue]-> State2 : Train Model Request
State2 : Trained model
State2 -[#blue]-> [*] : Delete Model Registration
State2 -[#blue]-> State3 : Re-train Model Request
State3 : Retrained model
State3 -[#blue]-> [*] : Delete Model Registration
@enduml
Model-Deployment
1. Using Kserve
Installing Kserve
./bin/install_kserve.sh
Verify Installation
~$ kubectl get pods -n kserve
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kserve-controller-manager-5d995bd58-9pf6x 2/2 Running 0 6d18h
Deploy trained qoe prediction model on Kserve
# Create namespace
kubectl create namespace kserve-test
Create qoe.yaml file with below contents
apiVersion: "serving.kserve.io/v1beta1"
kind: "InferenceService"
metadata:
name: "qoe-model"
namespace: kserve-test
spec:
predictor:
model:
modelFormat:
name: tensorflow
storageUri: "<MODEL URL>"
To deploy model update the Model URL in the qoe.yaml file and execute below command to deploy model
Refer Obtain Model URL for deploying trained models
kubectl apply -f qoe.yaml
Verify Model-Deployment
~$ kubectl get InferenceService -n kserve-test
NAME URL READY PREV LATEST PREVROLLEDOUTREVISION LATESTREADYREVISION AGE
qoe-model http://qoe-model.kserve-test.svc.cluster.local True 100 qoe-model-predictor-00001 42s
~$ kubectl get pods -n kserve-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
qoe-model-predictor-00001-deployment-86d9db6cb-5r8st 2/2 Running 0 93s
Test predictions using model deployed on Kserve
In order to test our deployed-model, we will query the InferenceService from a curl-pod.
# Deploy a curl-pod
kubectl run curl-pod --image=curlimages/curl:latest --command sleep 3600
# Query Inference-Service
kubectl exec -it curl-pod -- \
curl \
--location http://qoe-model.kserve-test.svc.cluster.local/v1/models/qoe-model:predict \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{
"signature_name": "serving_default",
"instances": [[
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56],
[2.56, 2.56]]
]
}'
Uninstall Kserve
./bin/uninstall_kserve.sh
For Advanced usecases, Please refer to official kserve-documentation here
2. Install both Kserve and Kserve adapter for deploying models (Optional/Not validated in k-release)
To install Kserve run the below commands Please note to update the DMS IP in example_recipe_latest_stable.yaml before installation
./bin/install_kserve_inference.sh
Uninstall both Kserve and Kserve adapter for deploying models
To uninstall Kserve run the below commands
./bin/uninstall_kserve_inference.sh
Steps to deploy model using Kserve adapter
Prerequisites
Install chart museum
Build ricdms binary
Run ric dms
export RIC_DMS_CONFIG_FILE=$(pwd)/config/config-test.yaml ./ricdms
Create sample_config.json
Create sample_config.json file with the following contents
{ "xapp_name": "sample-xapp", "xapp_type": "inferenceservice", "version": "2.2.0", "sa_name": "default", "inferenceservice": { "engine": "tensorflow", "storage_uri": "<Model URL>", "runtime_version": "2.5.1", "api_version": "serving.kubeflow.org/v1beta1", "min_replicas": 1, "max_replicas": 1 } } Refer :ref:`Obtain Model URL for deploying trained models <reference5>`
Copy sample_config.json
Update the below command with kserve adapter pod name
kubectl cp sample_config.json ricips/<kserve adapter pod name>:pkg/helm/data/sample_config.json
Generating and upload helm package
curl --request POST --url 'http://127.0.0.1:31000/v1/ips/preparation?configfile=pkg/helm/data/sample_config.json&schemafile=pkg/helm/data/sample_schema.json'
Check uploaded charts
curl http://127.0.0.1:8080/api/chartsDeploying the model
curl --request POST --url 'http://127.0.0.1:31000/v1/ips?name=inference-service&version=1.0.0'
Check deployed Inference service
kubectl get InferenceService -n ricips